Seeds
Why do plants have seeds?
Seed contain the young plant which allows the plant to reproduce
People use some seeds as food

Seeds come in a variety of shapes and sizes

The first type of seed is “naked seeds” whose seeds develop inside a cone

The second type of seed is an “enclosed seed.”

It can be encased by fruit or in a dry fruit like nuts

The third type of seed is an “aggregate fruit” like raspberries

Parts of the seed include the seed coat, the embryo, the radicle, hypocotyl, epicotyl, the cotyledon, endosperm and megagametophyte

The Root of the Matter
Vegetative matter consists of stems, roots and leaves.

The roots grow down because of gravity.

The roots grow down because of gravity.
Roots hold the plant in the ground, help them move water and nutrients from the ground and store energy


There are two basic types of roots fibrous (many roots almost the same size) and taproot (one long root which grows straight down into the soil)
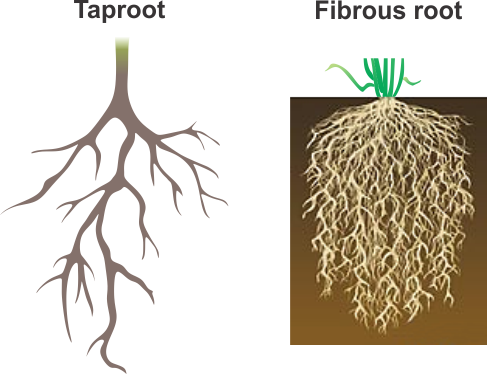

The main roots is known as the primary root and it may grow secondary roots. Each root is protected by root cap and many roots grow root hairs which absorb most of the water and nutrients

Some roots are attached to other plants. They anchor to the host plant and they can take water and minerals the air and from the host
Plants also grow in water. The roots still absorb water and minerals, but they don’t anchor the plant
Plants also grow in water. The roots still absorb water and minerals, but they don’t anchor the plant

Stems
Stems vary greatly in appearance. They grow up against gravity.
Stems have three jobs: Hold up leaves so they can get sunlight. They store food and water. And they most importantly transport food and water between the leaves and roots
Stems contain three types of tissue: Xylem which move water up and phloem which move food down. The third type of tissue is cambium which is the growth tissue that makes new xylem and phloem
There are two types of stems. Herbaceous plants have stem that are soft and green and can be bent because they don’t have a lot of xylem and phloem. These plants live only one year and are called annual plants.
The next type of stem is rough, woody and usually brownish. These are called woody plants. Includes trees and shrubs. They can live for many years and are called perennial plants. Xylem and phloem in perennial plants form rings around the stems. Each year another layer of xylem and phloem is made. This is why you can seed growth rings in plants which tell each year a plant has been alive.
Aerial stems grow straight above the ground. Runners grow along the ground. Grass and strawberries have runners.
Some stems are subterranean (grow underground). Bulbs are actually stems with many leaves.
Rhizomes grow away from the root beneath the ground. Sometimes rhizomes
Leaves
Leaves produce food for the plants using photosynthesis
Leaves have two parts the blade (flat thin green part) and petiole (small stem that attaches the blade to the plant)
Outside wax-like substance that prevents the leaf from losing water is called the cuticle
The first layer of plant cells is called the upper epidermis. This is where the cutin is made (stuff the cuticle is made of)
The middle of the leaf is called the mesophyll which has a of palisade cells near the upper epidermis and spongy cells below that. These tissues have the chlorophyll
The final layer of the epidermis is called the lower epidermis. It has tiny holes called stomata. It also has guard cells which determine the size of the stomata
The stomata do several jobs. For example, the allow carbon dioxide into the plant and release oxygen. And they finally they release water through a process called transpiration
Plants can transpire a lot of water
A simple leaf has only one leaf blade
Leaves that have more than one leaf are called a compound leaf. If the leaf blades are arranged in rows on both sides, it is called pinnately compound leaf. If the leaf blades start at a central point its called a palmately compound leaf
Parallel veins are duh… parallel (like train tracks)
Net veined leaves have a single main vein with smaller veins branching off of it. Pinnately-veined leaves has one main vein with smaller veins branching off. Palmately-veined leaves have more than one main vein with smaller veins branching off
Veins in leaves have two purposes. First, they help support the leaf so it can get enough sunlight. Second, they help water, nutrients and glucose travel through the plant
Alternating leaves have the first leaf attached to one side of the stem and the next leaf is attached to the other side of the stem.
Spiraling leaves seem to circle around the plant at their point of attachment.
Oppositional leaves attach at the same level, but at opposite sides of the stem.
Decussate leaves attach at a right angle to the previous leaves.
Whorled leaves have more than two leaves attached to the stem at the same level.
Spiraling leaves seem to circle around the plant at their point of attachment.
Oppositional leaves attach at the same level, but at opposite sides of the stem.
Decussate leaves attach at a right angle to the previous leaves.
Whorled leaves have more than two leaves attached to the stem at the same level.